Why it’s a problem that pulse oximeters don’t work as well on patients of color
New research ties inaccuracies in pulse oximeter readings to racial disparities in treatment and outcomes.
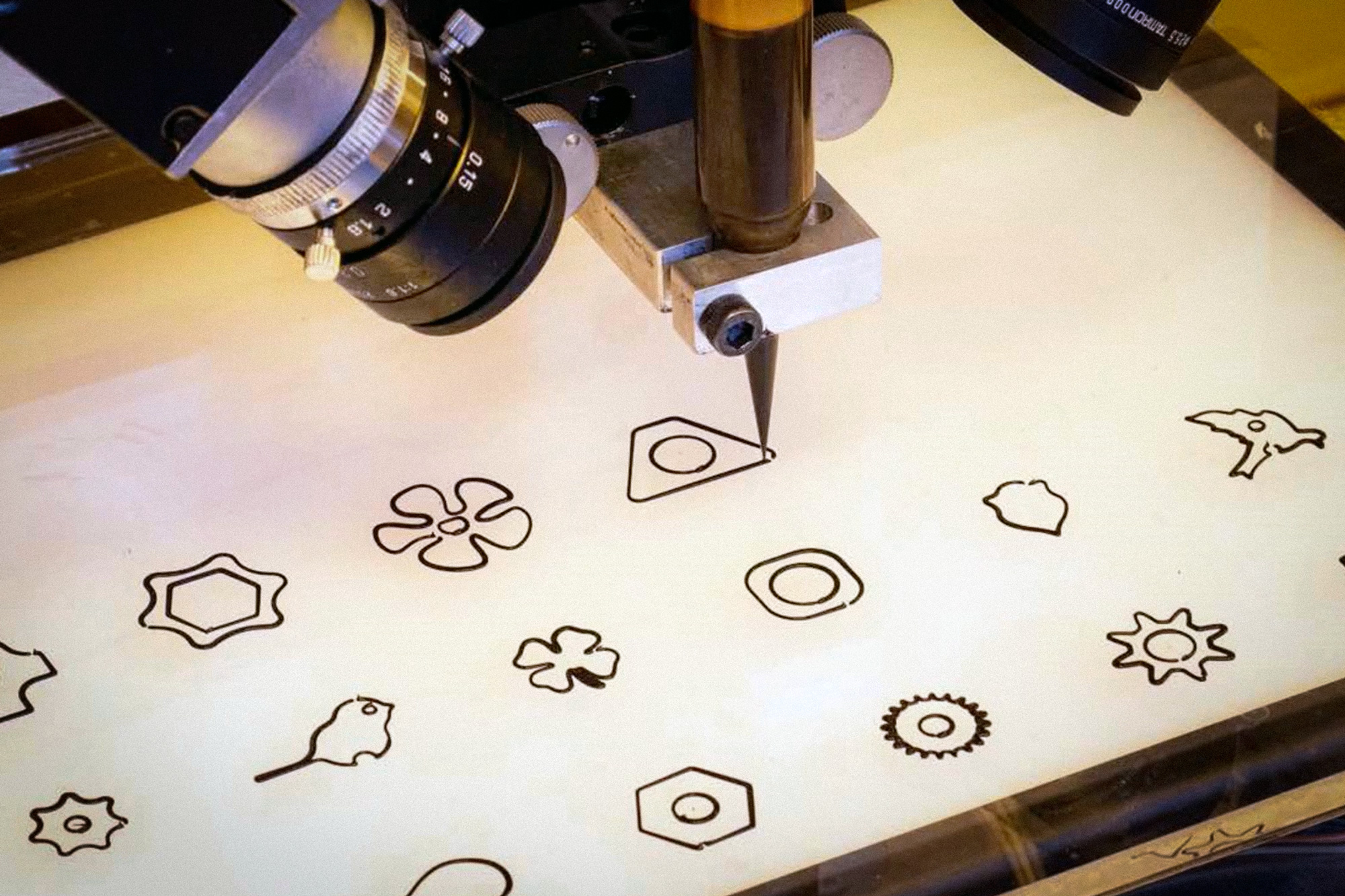
Using artificial intelligence to control digital manufacturing
Researchers train a machine-learning model to monitor and adjust the 3D printing process to correct errors in real-time.
Engineers repurpose 19th-century photography technique to make stretchy, color-changing films
The technique opens a door to manufacturing of pressure-monitoring bandages, shade-shifting fabrics, or touch-sensing robots.
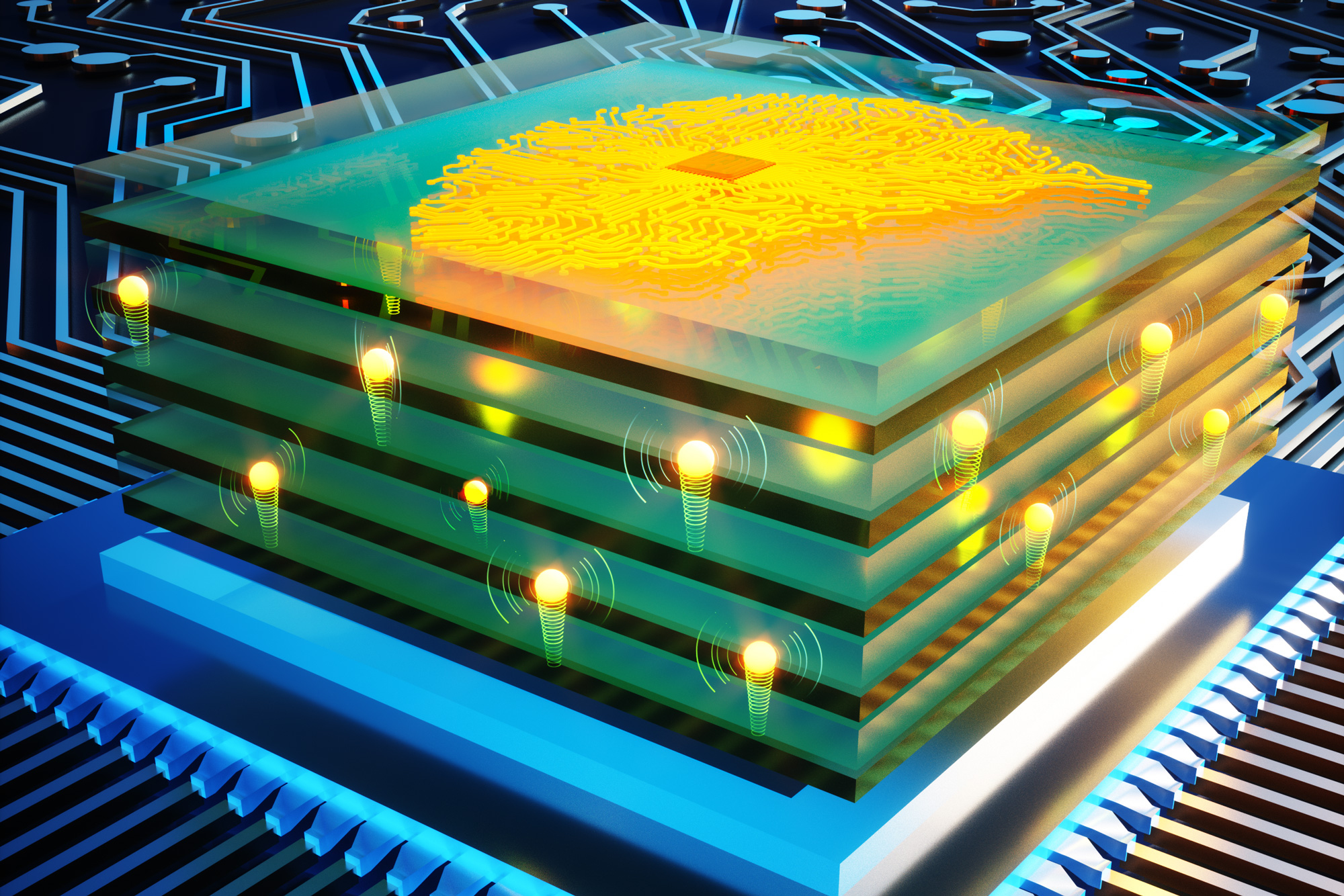
New hardware offers faster computation for artificial intelligence, with much less energy
Engineers working on “analog deep learning” have found a way to propel protons through solids at unprecedented speeds.
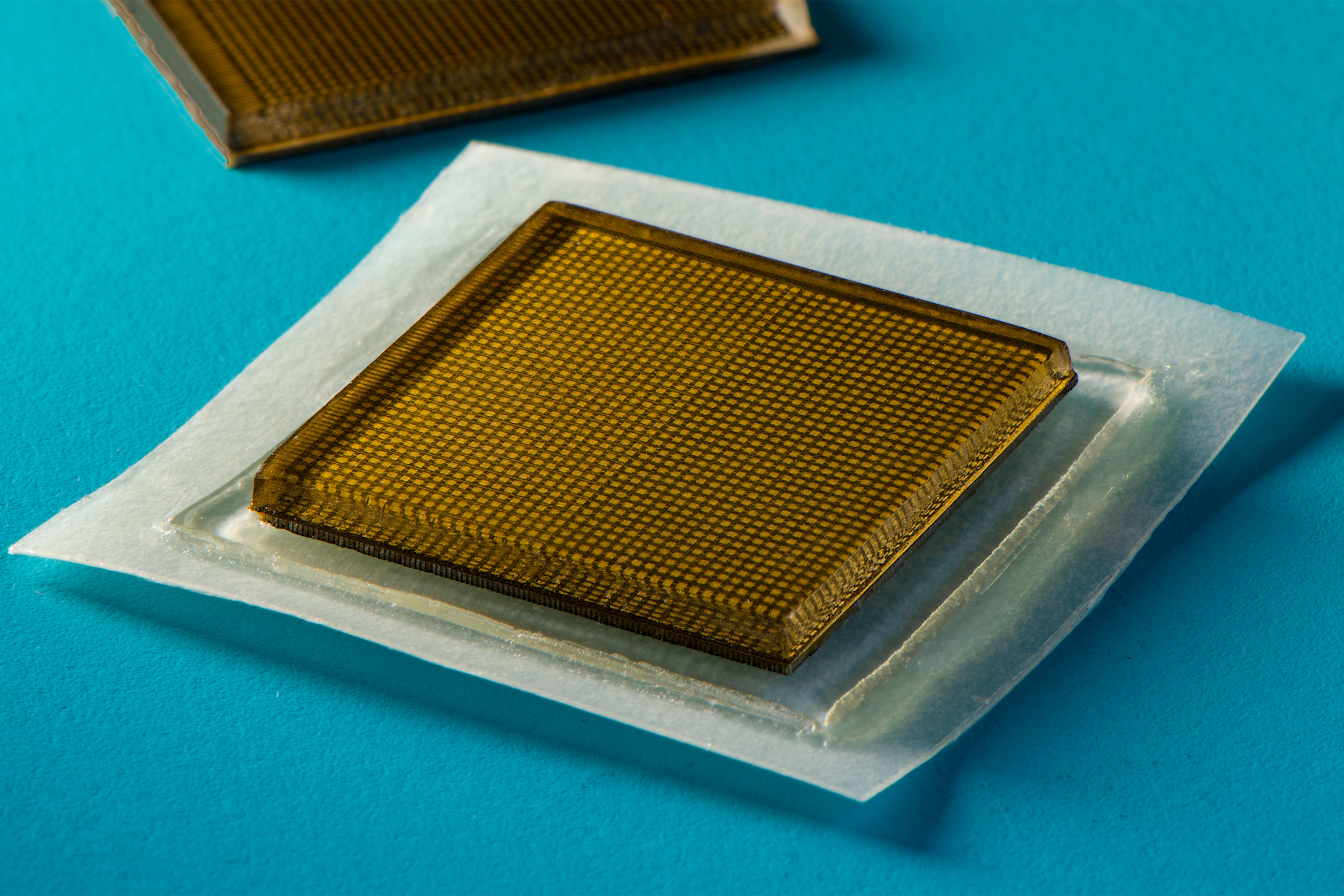
MIT engineers develop stickers that can see inside the body
New stamp-sized ultrasound adhesives produce clear images of heart, lungs, and other internal organs.
A global resource for better transportation systems
The MIT Mobility Initiative welcomes five inaugural industry members to advance safe, clean, and inclusive mobility.
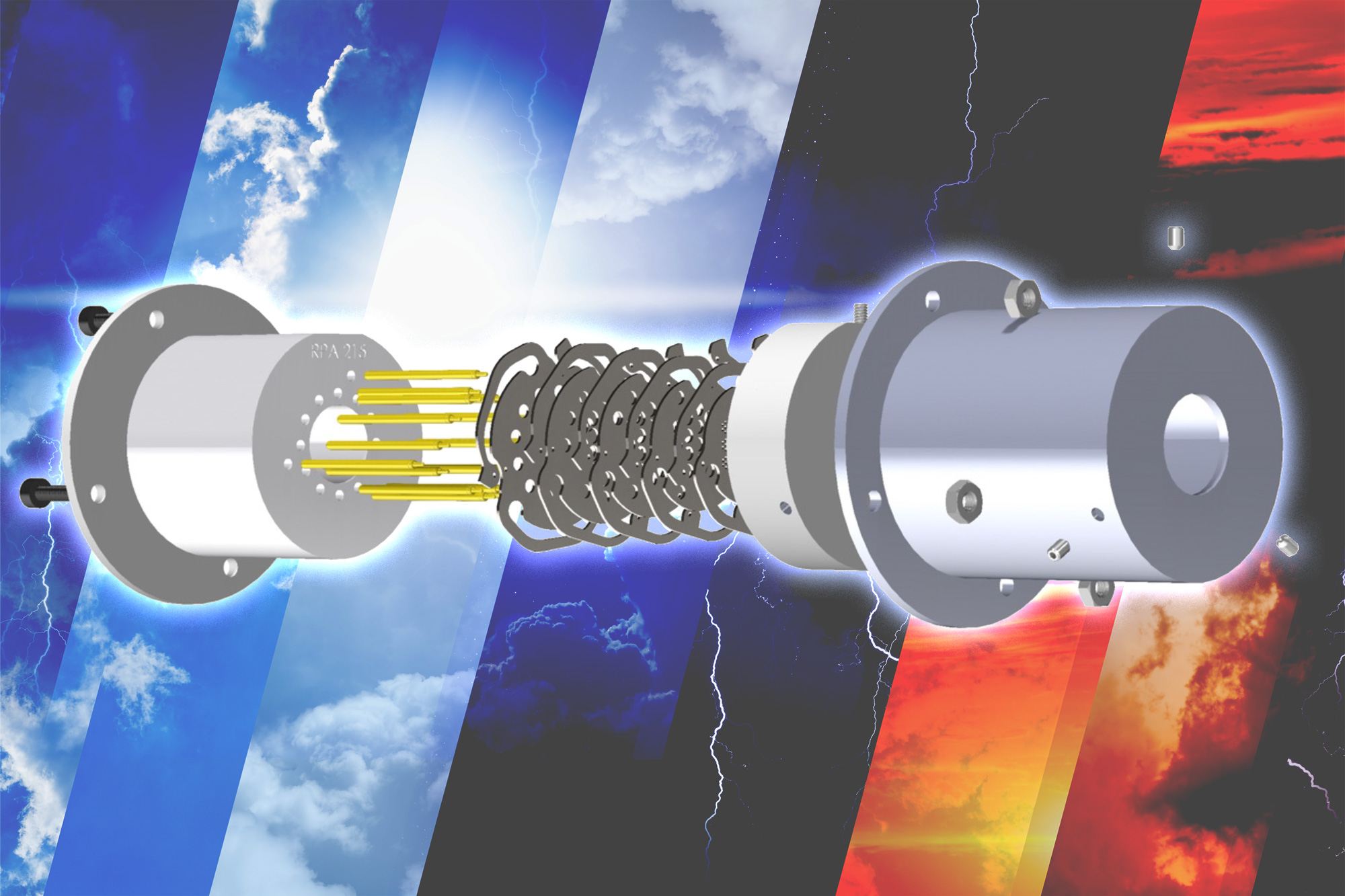
Researchers 3D print sensors for satellites
Cheap and quick to produce, these digitally manufactured plasma sensors could help scientists predict the weather or study climate change.
Q&A: Warehouse robots that feel by sight
Neuroscience professor and Science Hub investigator Ted Adelson explains how simulating the sense of touch with a camera can make robots smarter.
School of Engineering second quarter 2022 awards
Faculty members recognized for excellence via a diverse array of honors, grants, and prizes.
Explained: How to tell if artificial intelligence is working the way we want it to
“Interpretability methods” seek to shed light on how machine-learning models make predictions, but researchers say to proceed with caution.